-
While analysts agree banks are in better shape than in 2008, lawmakers are dusting off a crisis-era tool used by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corp. to soothe potential liquidity fears during the coronavirus pandemic.
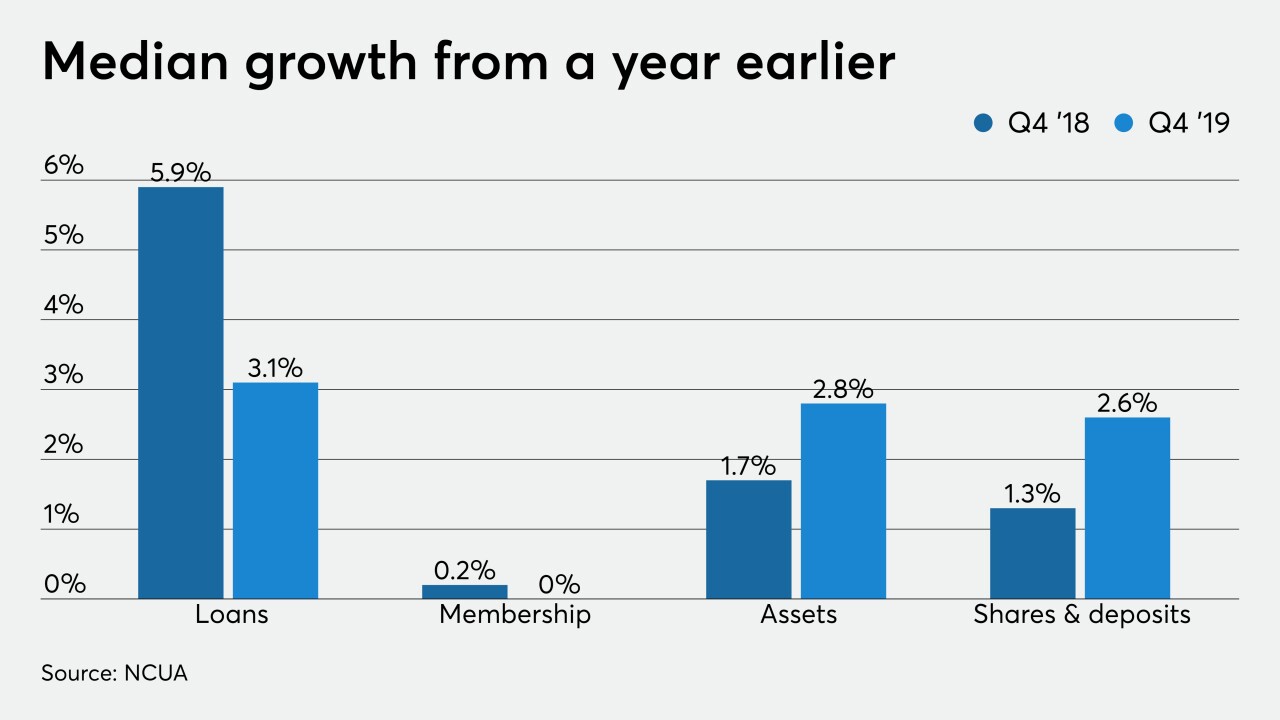
March 25 -
While loans continued to increase, growth was slower than one year previously and membership was flat.
March 25 -
Bankers will be pressed on upcoming earnings calls to forecast how the coronavirus pandemic — and the government's response — will shape credit quality, margins and fee income.
March 25 -
Margins will be squeezed after the Federal Reserve lowered interest rates earlier this month to counteract the economic fallout from the coronavirus.
March 25 -
The central bank will prioritize monitoring and outreach while reducing examination activity due to the coronavirus pandemic until at least the end of April.
March 24 -
The Fed announced several new lending facilities and virtually “unlimited” purchases of Treasury bonds; Ana Botín will donate the money to a coronavirus fund.
March 24 -
The central bank's sweeping actions suggest a cash shortage gripping sectors directly hit by the pandemic. Banks were supposed to be protected by Dodd-Frank but are still vulnerable to a funding domino effect.
March 23 -
The Federal Housing Finance Agency authorized the government-sponsored enterprises to lend additional support to the mortgage-backed securities market and temporarily allow some flexibility in lending requirements to address coronavirus-related concerns.
March 23 -
The Federal Reserve committed Monday to conducting more asset purchases of Treasury securities and mortgage-backed securities and announced $300 billion in new financing for credit facilities.
March 23 -
The Federal Reserve committed Monday to conducting more asset purchases of Treasury securities and mortgage-backed securities and announced $300 billion in new financing for credit facilities.
March 23