-
The FHFA’s forbearance extension to September is forcing nonbank servicers to buy out more delinquent loans. It's also upended loss estimates for investors and made racial and income disparities in the mortgage market worse.
March 25 -
The agency will allow an additional three months of forbearance for loans backed by Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, giving homeowners up to 18 months to suspend payments due to the pandemic.
February 25 -
The decision provides more clarity to noteholders in the state about when the six-year statute of limitations to bring a foreclosure action begins.
February 23 -
While loan performance is improving in aggregate, some borrowers remained unaware of the relief available or were unable to access it, according to the Research Institute for Housing America.
February 8 -
The legislation would let banks postpone the start date of the Current Expected Credit Losses accounting standard and delay categorizing pandemic-related loan modifications as troubled debt restructurings.
December 23 -
The Consumer Financial Protection Bureau has taken a hands-off approach to servicers during the pandemic. But with forbearance plans set to expire and President-elect Biden likely to appoint new CFPB leadership, companies lacking aggressive plans to help borrowers could face tougher enforcement.
December 8 -
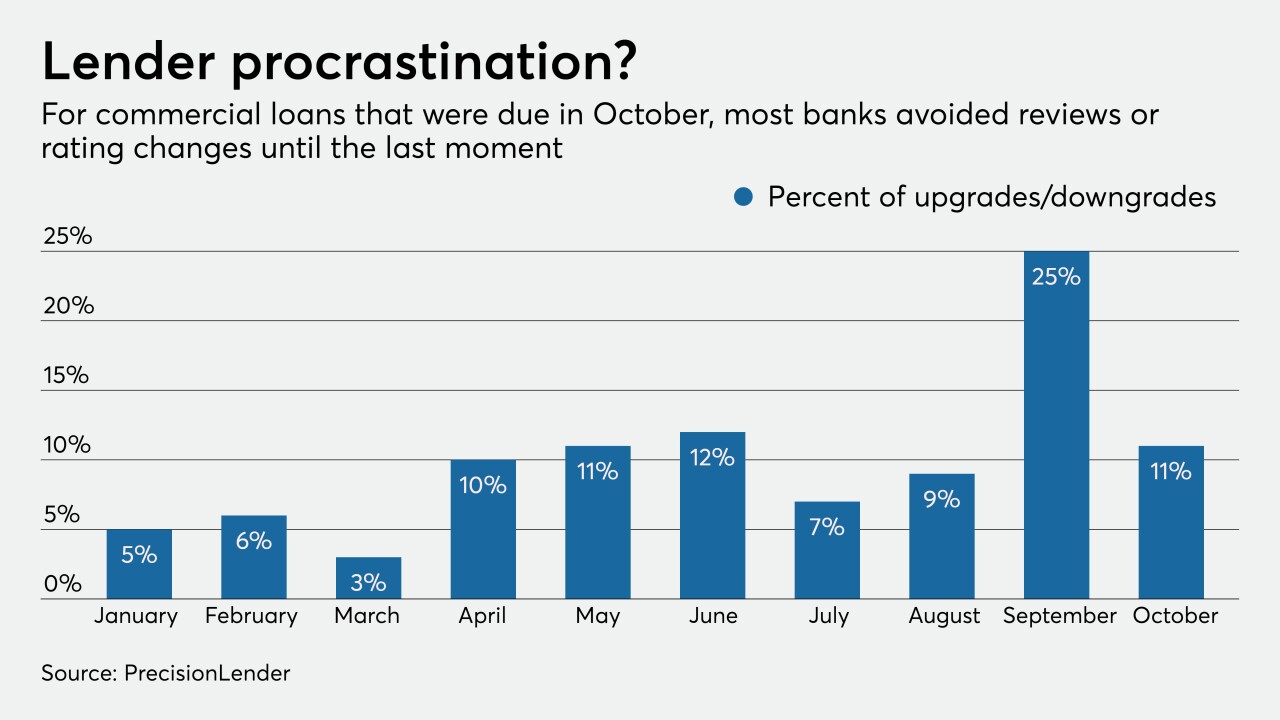
Some lenders are poring over commercial portfolios more frequently than normal — perhaps as often as once a month — to uncover problems hidden by payment deferrals and government stimulus before it's too late.
December 8 -
On the same day that Mr. Cooper announced a settlement with state and federal authorities over its servicing practices, the Dallas company, U.S. Bank and PNC reached separate agreements with DOJ regarding bankrupt borrowers.
December 7 -
The economic fallout from COVID-19 has highlighted systemic concerns about commercial real estate exposure, business debt and short-term wholesale funding, the Financial Stability Oversight Council said in an annual report.
December 3 -
Default risks soar in minority neighborhoods during challenging economic times because, data shows, homes there are overpriced relative to incomes. Zoning and other changes could make loans more affordable by boosting housing stock and driving down prices.
November 25 American Enterprise Institute’s Housing Center
American Enterprise Institute’s Housing Center